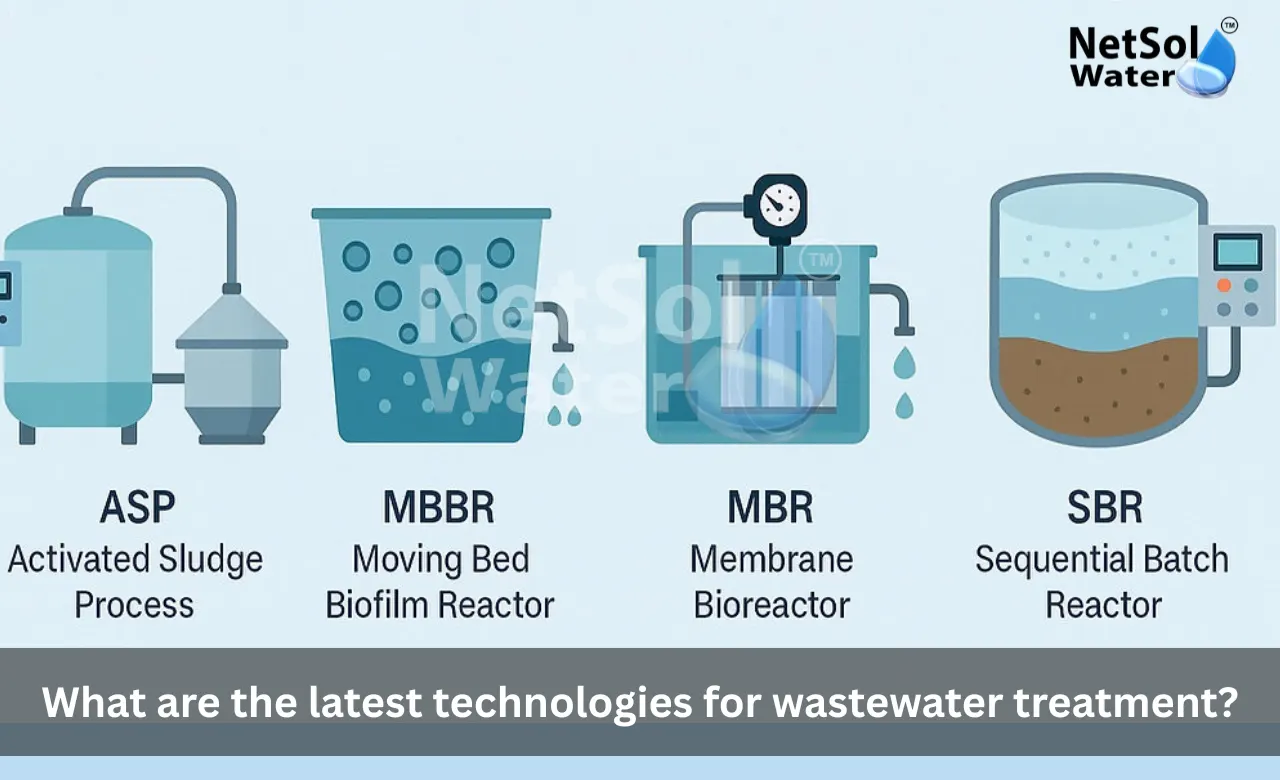
Why am I thirsty after drinking RO water?
Many people feel thirsty after they drink water from an RO plant. This surprises new users and can leave them wondering if the water is safe. RO water removes most dissolved solids and minerals from source water. It can remove 92 to 99 percent of minerals and salts, which gives very pure water. We are the leading commercial RO plant manufacturer, and we see this question often from customers and site teams. We will explain why people feel thirsty after drinking RO water and what steps you can take to fix the problem.
Lack of Electrolytes and Mineral Content
Water that lacks minerals changes hydration in the body. This point matters for anyone who uses a commercial RO system for drinking or for processes that need balanced water. Let us have a look at some reasons and effects that follow from low mineral content.
1. Electrolytes and Hydration
Electrolytes such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium help the body move water into cells and keep fluids balanced. When water has very low mineral content, the body may not absorb it as efficiently. This can leave a person feeling thirsty again soon after drinking. The mouth may also not sense the usual mineral balance, so the brain does not send strong signals that hydration is complete. People who drink only demineralized water may notice this pattern during hot weather or after exercise. The solution is not to avoid RO water but to add back small amounts of minerals so the body gets the signals it expects.
2. Taste
Mineral-free water can taste flat and thin when compared with mineral-rich water from springs or a filtered municipal supply. That quality can make people feel like they still need a drink. The lack of flavour cues can mislead the senses. Taste works as a feedback system. When water tastes lively, the mouth tells the brain that the body has received a proper drink. When water tastes flat, the brain may not register that the body no longer needs fluid. This effect matters in homes and in offices where people expect water to feel satisfying.
Physiological Responses and Mineral Leaching
Understanding how the body reacts to demineralized water helps explain persistent thirst. Let us have a look at some mechanisms.
1. Body Absorption and Signalling
The body senses fluid balance through blood volume and electrolyte levels. When electrolyte levels drop, the body triggers thirst to prompt drinking. Drinking pure water without electrolytes can temporarily dilute blood electrolyte levels. That dilution may trigger more thirst or a desire for food that contains minerals. The effect may be stronger in people who already have low mineral intake from food. In daily life, this means that simply increasing plain water intake may not fix the feeling. The body may need small amounts of sodium, magnesium, or potassium to restore balance and stop signalling thirst. For many people, adding trace minerals to water solves the issue by restoring the balance that the body expects.
2. Mineral Leaching Hypothesis
Some researchers discuss whether very pure water can pull tiny amounts of minerals from food or from the body as it passes through the digestive system. The evidence is limited, but the idea explains why some people report a persistent dry feeling after long-term use of demineralized water. If demineralized water does absorb trace ions, the net effect over a day would be small for most people who eat a balanced diet. The practical implication is clear. If you use RO water for all drinks and cooking, then you should monitor mineral intake from food and consider adding a remineralization step to the water system so the water itself contributes useful minerals.
Contamination and System Maintenance
Water quality depends not only on mineral content but also on how well the system performs. Poor maintenance can change water taste and lead to sensations that feel like thirst. Let us have a look at some maintenance points and corrective steps.
1. Bacterial Growth and Filters
An RO plant needs regular filter and membrane service. If filters clog or membranes age, the water can pick up odd tastes that make it feel unclean. Bacterial growth can occur in stagnant parts of a system that see little flow. That growth can create a film that alters mouthfeel. Users then describe the water as tasting off and report thirst after drinking. The remedy is routine service and periodic sanitization of the tank and piping. Commercial sites should follow a maintenance schedule that matches their water use and local water quality. We are the leading commercial RO plant manufacturer, and we design plants with easy access points for service and clear guidelines for filter replacement.
2. System Upgrades and Remineralization
Adding a remineralizer after the RO membrane gives water a low-level mineral profile that the body finds satisfying. Remineralizers use minerals such as calcium and magnesium to restore taste and hydration cues. Sites can also use trace mineral drops that dissolve in the water at the point of use. Another option is to blend a small percentage of mineral-rich feed water with RO water to reach a desired profile. All these choices reduce thirst and improve user comfort.
How to Fix It
Fixes that restore comfort matter for both individual users and facility managers. Implementing the right fix will improve user satisfaction and keep hydration stable. Let us have a look at some effective and easy-to-use remedies.
1. Use a Remineralizer or Mineral Drops
A remineralizer cartridge adds controlled amounts of calcium and magnesium after the RO stage. This step improves taste and helps the body sense that hydration is complete. Mineral drops serve the same role for small-scale use. People can add a few drops per glass for daily drinking. For offices and public points of use, a cartridge keeps water consistent across all users.
2. Ensure Proper Maintenance and Balance with Diet
Changing prefilters and RO membranes at recommended intervals will keep water clean and fresh. Sanitizing the storage tank will prevent bacterial growth that can affect taste. At the same time, maintain a diet with leafy greens, nuts, and dairy or fortified foods so you meet daily needs for magnesium and calcium. These foods support hydration and reduce dependence on water minerals alone.
Read some interesting information for the Effluent Treatment Plant Manufacturer in Noida
Conclusion
RO water provides very pure water, and that purity can change how your body senses hydration. Adding a simple remineralization step will usually stop the cycle of thirst after drinking. We are the leading commercial RO plant manufacturer, and we design plants that restore mineral balance and meet site needs. If your team or home faces this issue, you can contact us for a consultation. We will help you choose a solution that fits your water source and user comfort. Request a consultation today to learn more about commercial-scale remineralization and routine service options.
Contact Netsol Water at:
Phone: +91-9650608473
Email: enquiry@netsolwater.com