The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Environmental Change has advised the updated CPCB Guidelines for Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETPs) working at different industrial clusters in the country. The primary point of the revised standards is to minimize water contamination. These standards were finalized after extensive consultations with industries and different partners and detailed deliberations with the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). The changed norms were notified on January 1, 2016. The changed norms will help fundamentally work on the performance of CETPs through the implementation of design inlet quality, resolving the issues of coastal pollution because of industrial discharges, and keeping a close watch on the effect of the release of industrial effluent on soil and groundwater quality.
The Guidelines given for CETP by CPCB Guidelines for Common Effluent Treatment Plants are as per the following:
CPCB Guidelines for Common Effluent Treatment Plants
1- The Centre has advised the revised standards for Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETPs) working at different industrial groups in the country with an aim to minimize water contamination.
2- The Environment Ministry notified the norms which were concluded after broad counsel with industries and other partners and point-by-point thoughts with the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
3- “The Environment Ministry has notified the revised standards for Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETPs) working at different industrial groups in the country. The primary point of the revised standards is to minimize water contamination,” an official statement said today, adding that the revised standards were notified on January 1.
4- The revised standards will help in essentially working on the performance of CETPs through the implementation of design inlet quality, addressing the issues of coastal contamination because of industrial discharges.
5- It will also help in further improving the CETP’s performance by close watch on the effect of the discharge of industrial effluent on soil and groundwater quality.
6- Under the revised standards, an provision of soil and groundwater quality checking two times per year (pre-and post-monsoon) has been introduced.
7- This has been introduced with a concentrate on the effect of removal of treated effluent on land, in case of the method of removal is ‘on land for irrigation’ and the monitoring will be done by the separate CETP management.
8- “The method of ‘Discharge into the ocean’ (marine outfalls) giving extremely high dilution will qualify all requirements for a relaxed maximum permissible concentration of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD).
9- “The maximum permissible concentration of Fixed Dissolved Solids (FDS) by constituent units to CETP has been determined as far as maximum admissible contribution value,” the statement added.
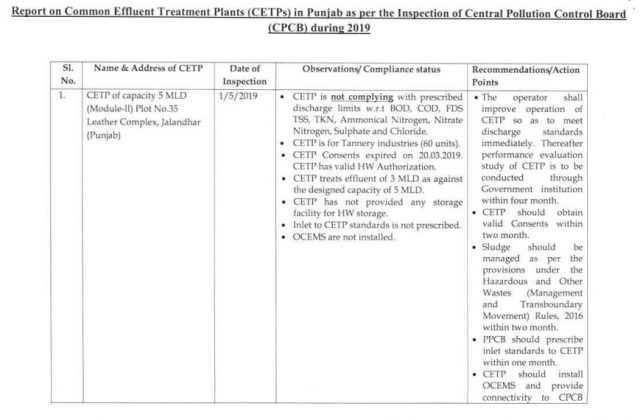
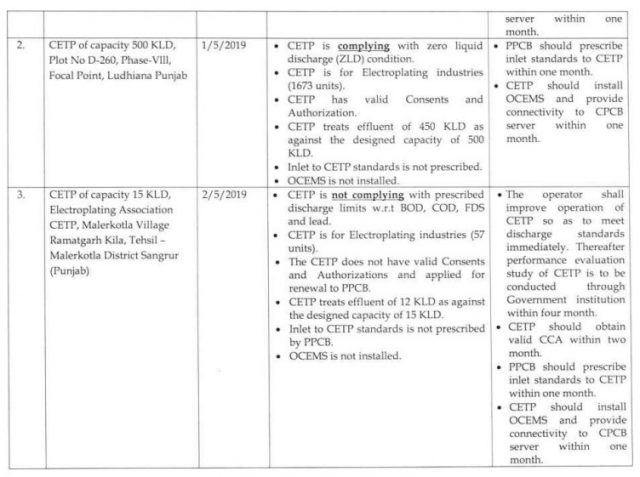
10- Status report by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) consistent with the National Green Court order May 21, 2020, in Original Application No. 593/2017 (Paryavaran Suraksha Samiti and Others Vs Union of India and Others) with Original Application No. 148/2016 (Mahesh Chandra Saxena Vs South Delhi Municipal Corporation and Others).
11- The report of September 16, 2020, contained the state-wise consistency status of all industries generating trade effluent and requiring effluent treatment plants (ETP) – as reported by the state pollution control board (SPCB)/pollution control committee (PCC). According to the information got from SPCBs/PCCs:
- Out of a total 64,484 number of industries requiring ETPs, 62,653 industries are working with functional ETPs and 1,831 industries are working without ETPs.
- 61,530 industries are complying with environmental norms and 1,123 industries are noncomplying.
- There are a complete 191 CETPs, out of which 129 CETPs are agreeing with environmental standards and 62 CETPs are non-complying.
- There is a total of 15,730 STPs (including municipal and other than municipal (non-municipal/independent) STPs), out of which, 15,200 STPs are agreeing with environmental guidelines and 530 STPs are non-complying.
- There are 84 CETPs in the construction/proposal stage, whereas, for STPs, 1,081 tasks (municipal and non-municipal) are under the construction/proposal stage.
The report also contained an assessment of the effect of the lockdown on the water quality of major rivers. During the pre-lockdown period (March 2020), SPCBs gathered samples from 388 locations through 366 samples from the checking locations during lockdown (April 2020) from 19 major rivers, and collected samples were analyzed for Primary Water Quality Measures for Washing Water Quality Standards notified under the Environment (Protection) Rules, 1986.