Micropollutants, PFAS & the Next Generation of Wastewater Treatment
Micropollutants move through sewers, rivers and treatment plants. Cities in India face growing pressure to control these traces while they grow their industries and homes. Wastewater Treatment plants must do more than remove dirt and organic matter. They must detect, reduce and stop chemicals that affect people. Netsol Water is the leading name in practical solutions for modern problems. We will explore why micropollutants matter, what PFAS mean and how the next generation of Wastewater Treatment can meet the challenge.
Micropollutants
Micropollutants pose a special test for current treatment systems. They appear at very low levels. People face long term risks when drinking water carries persistent residues. This makes micropollutants a high priority for cities and industry. Let us have a look on some key areas that define the work to remove these traces and protect water users.
Sources and risks
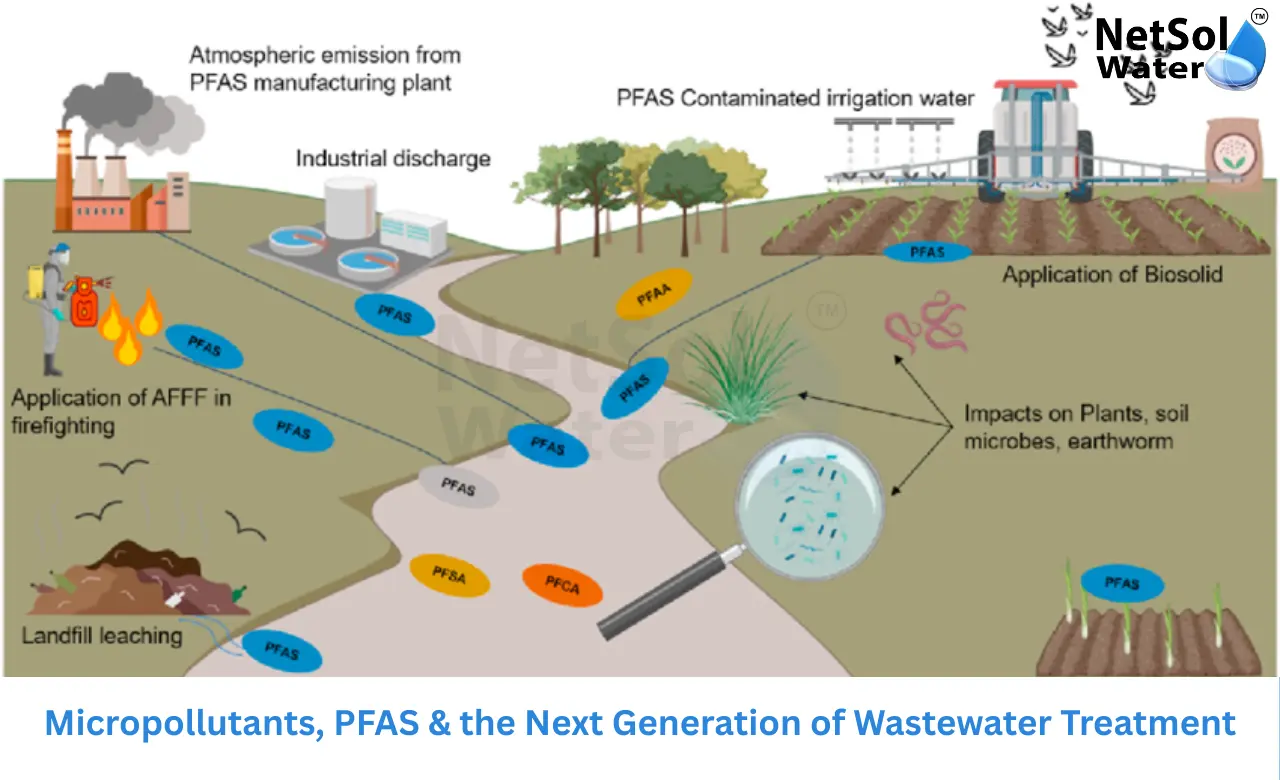
Micropollutants come from many everyday activities. Medicines that people flush down, toilets, personal care items left in drains and chemical runoff from farms all add to the load. Small amounts reach rivers and lakes. Over time those amounts add up. Some compounds interact with human hormone systems. This creates a demand for better detection and for treatment steps that can handle specific chemical classes. Plant operators must map sources track loads and plan targeted upgrades. Communities must also reduce source inputs by changing use patterns and disposal habits.
Detection and removal challenges
Detecting micropollutants requires precise tools and trained staff. Labs must use instruments that can see parts per trillion. Many treatment plants lack this capacity. Even when detection happens removing the chemicals proves hard. Some compounds resist normal biological treatment. Others break into fragments that still cause harm. Advanced steps like adsorption advanced oxidation and membrane processes can work. Each method has strengths and trade offs. For example adsorption captures many compounds but needs safe disposal of the used material. Advanced oxidation breaks molecules but uses energy and chemicals. Plant teams must choose methods that match the compound profile the plant scale and local budgets.
PFAS
PFAS represent one of the clearest modern threats among micropollutants. These chemicals do not break down easily. They move through water and build up in soil and living bodies. Many industries used PFAS for years in products and processes. Now regulators and communities press for action. Let us have a look on some elements that show why PFAS need focused plans and how treatment can address them.
What PFAS are and why they matter
PFAS stand for per and poly fluoroalkyl substances. People used them in firefighting foams, cookware, coatings and fabrics. These molecules resist heat water and chemical attack. That resistance makes them useful and also dangerous. They stay in the environment for a long time. Scientists link some PFAS to health issues when people face long term exposure. Local water supplies can carry PFAS near industrial sites airports and waste disposal areas. Authorities now measure PFAS more widely. Plant operators need clear protocols to test for PFAS and to stop them from passing through to drinking water.
Treatment approaches for PFAS
Treating PFAS requires more than one tool. Adsorption on granular media and on synthetic resins can trap many PFAS molecules. Membrane filtration can concentrate PFAS so operators can manage them more safely. Advanced oxidation sometimes helps to break long chains into simpler pieces but not all PFAS respond well. Safe disposal or destruction of the PFAS rich waste stream matters as much as the capture step. Options include thermal destruction or secure landfilling under strict controls. A clear program must combine source control monitoring and treatment choice. That program also needs trained staff and steady funding.
Next Generation of Wastewater Treatment
The next generation of Wastewater Treatment must match the new chemical threats and the need for clean water for growing cities. New plants must merge proven processes with digital tools and flexible designs. They must aim for lower energy use lower waste and better removal of micropollutants and PFAS. Let us have a look on some practical technologies and systems that plants can adopt to meet the new goals.
Advanced treatment technologies
Plants can add modules that target hard to remove chemicals. Adsorption units using personalized media can pull out a wide range of micropollutants. Membrane systems can separate tiny particles and concentrate harmful compounds. Advanced oxidation processes can break many complex molecules into simpler pieces that biology can then remove. Operators can combine these methods in series to gain wider coverage. The choice depends on the chemicals present the plant size and the available budget. Upgrading existing plants with compact modules helps cities avoid full scale rebuilds. This approach makes upgrades faster and lowers initial investment.
Digital monitoring and decentralized systems
Smart sensors and data platforms change how plants run. Real time monitoring can show spikes in chemical loads. Operators can then shift treatment steps instantly. Decentralized systems can treat water closer to the source. This cuts transport and reduces the release of chemicals into shared sewers. Small modular units work well for industrial parks large buildings and remote communities. Netsol Water is the leading provider that uses practical design with modular delivery and with digital control.
Read some interesting information for Effluent Treatment Plant Manufacturer in Faridabad
Conclusion
Clean water for people and nature depends on solid Wastewater Treatment that meets new chemical risks. Authorities plant operators and technology providers must work together. Netsol Water is the leading partner for many cities and industries that need clear plans upgrades and training. If you want to learn how to detect measure or remove micropollutants or PFAS contact Netsol Water for a consultation.
Contact Netsol Water at:
Phone: +91-9650608473
Email: enquiry@netsolwater.com